Correspondence-Free Non-Rigid Point Set Registration Using Unsupervised Clustering Analysis
2Shandong University 3Peking University
4Institute of Automation, Chinese Academy of Sciences
5University of Chinese Academy of Sciences
Abstract
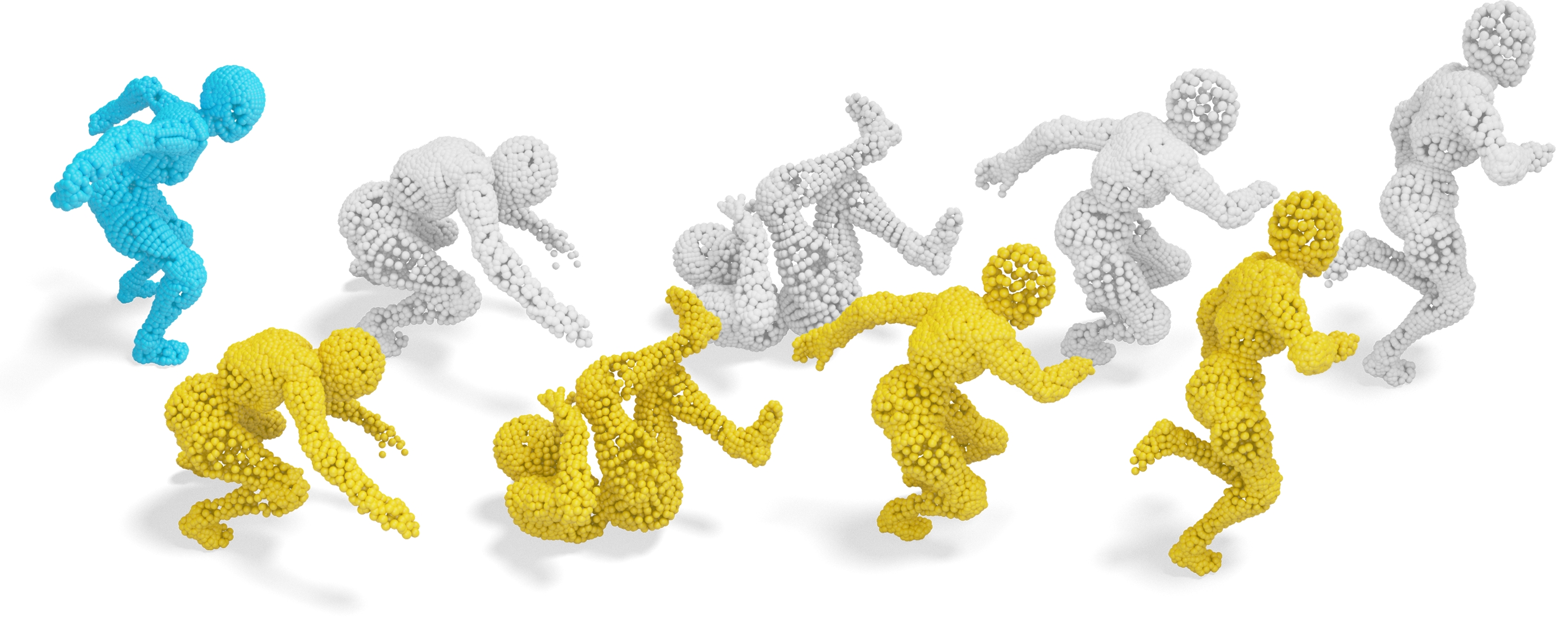

This paper presents a novel non-rigid point set registration method that is inspired by unsupervised clustering analysis. Unlike previous approaches that treat the source and target point sets as separate entities, we develop a holistic framework where they are formulated as clustering centroids and clustering members, separately. We then adopt Tikhonov regularization with an ℓ1-induced Laplacian kernel instead of the commonly used Gaussian kernel to ensure smooth and more robust displacement fields. Our formulation delivers closed-form solutions, theoretical guarantees, independence from dimensions, and the ability to handle large deformations. Subsequently, we introduce a clustering-improved Nystr ̈ om method to effectively reduce the computational complexity and storage of the Gram matrix to linear, while providing a rigorous bound for the lowrank approximation. Our method achieves high accuracy results across various scenarios and surpasses competitors by a significant margin, particularly on shapes with substantial deformations. Additionally, we demonstrate the versatility of our method in challenging tasks such as shape transfer and medical registration.
Motivation
Non-rigid point set registration is to optimize a non-linear displacement field that accurately aligns one geometric shape with another. However, given two point sets, one acting as the source and the other as the target, non-rigid registration presents a highly ill-posed and much more complex challenge compared to the rigid counterpart. This increased complexity is primarily attributed to the additional freedom of deformations allowed in non-rigid registration, especially when dealing with shapes that exhibit large deformations. Previous approaches typically perform shape matching first and then estimate the alignment transformation based on the established correspondences via off-the-shelf registration techniques. Nevertheless, shape matching self has many outliers that may deteriorate registration. To address this problem, we explore a direct registration method for handling large deformations, without relying on shape matching.
Problem Formulation
Results
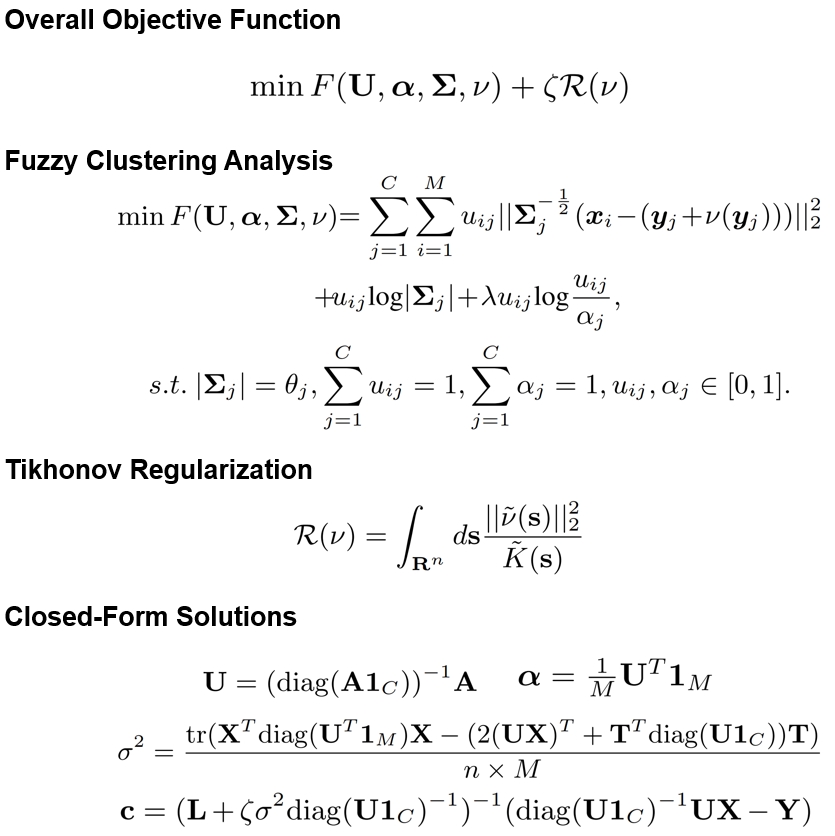
Qualitative comparisons on the FAUST dataset. The top and the bottom rows represent the test registrations of intra and inter-subject, respectively.
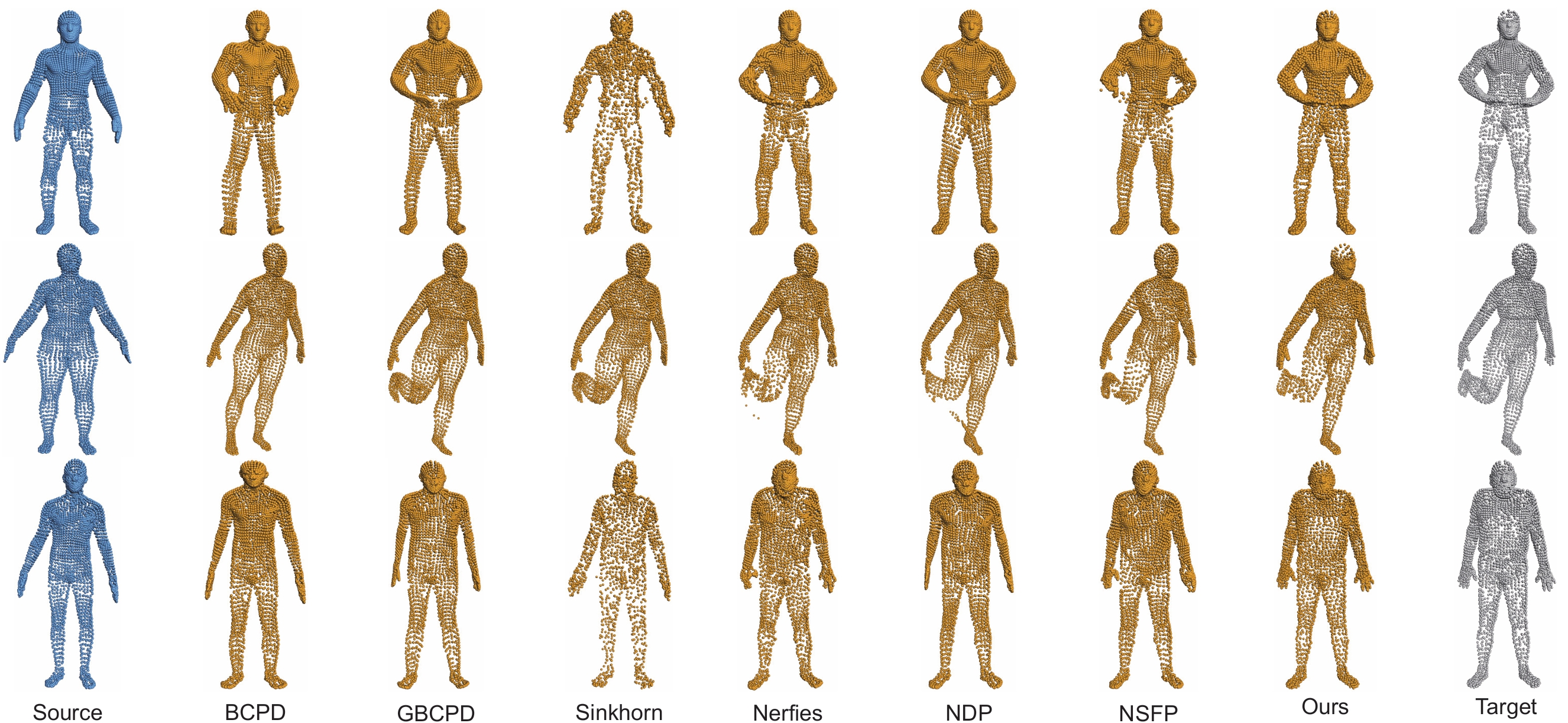
Quantitative comparisons on the real-world FAUST human scan dataset.
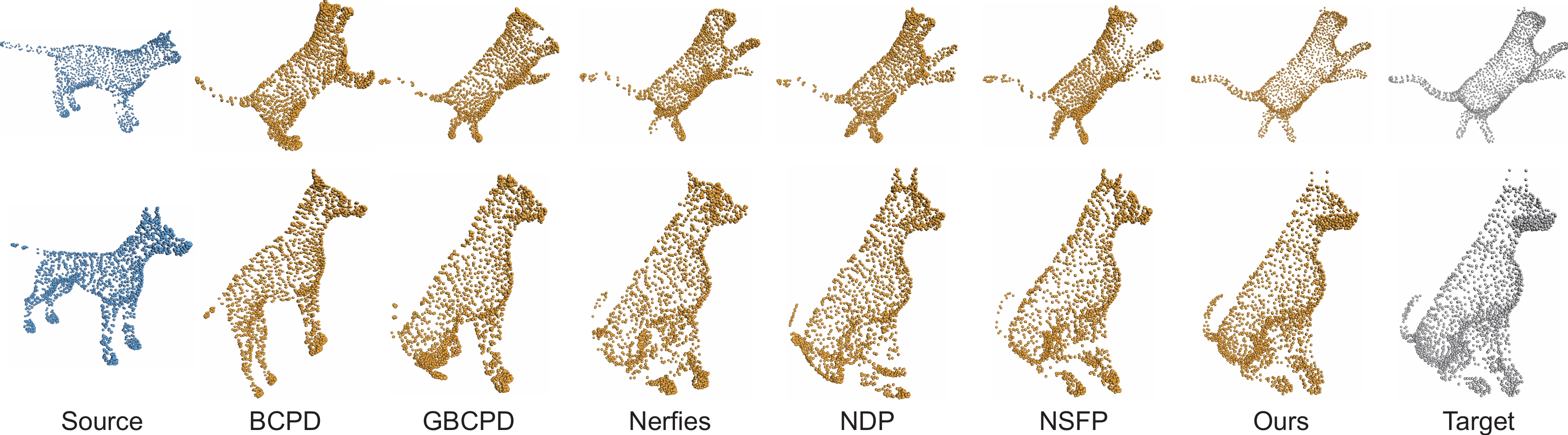
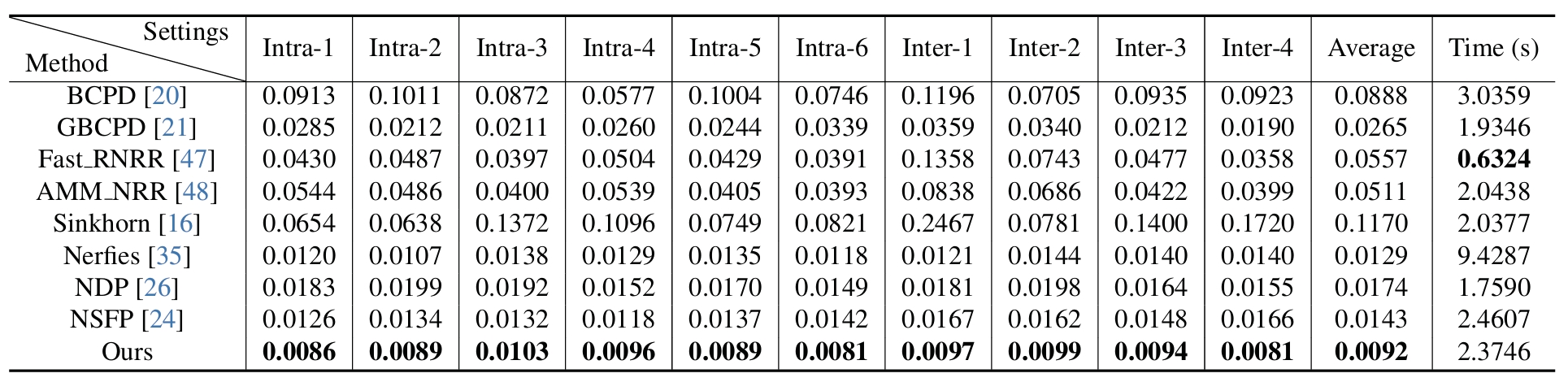
Qualitative comparisons on the TOSCA dataset, where much larger shape deformations exist.
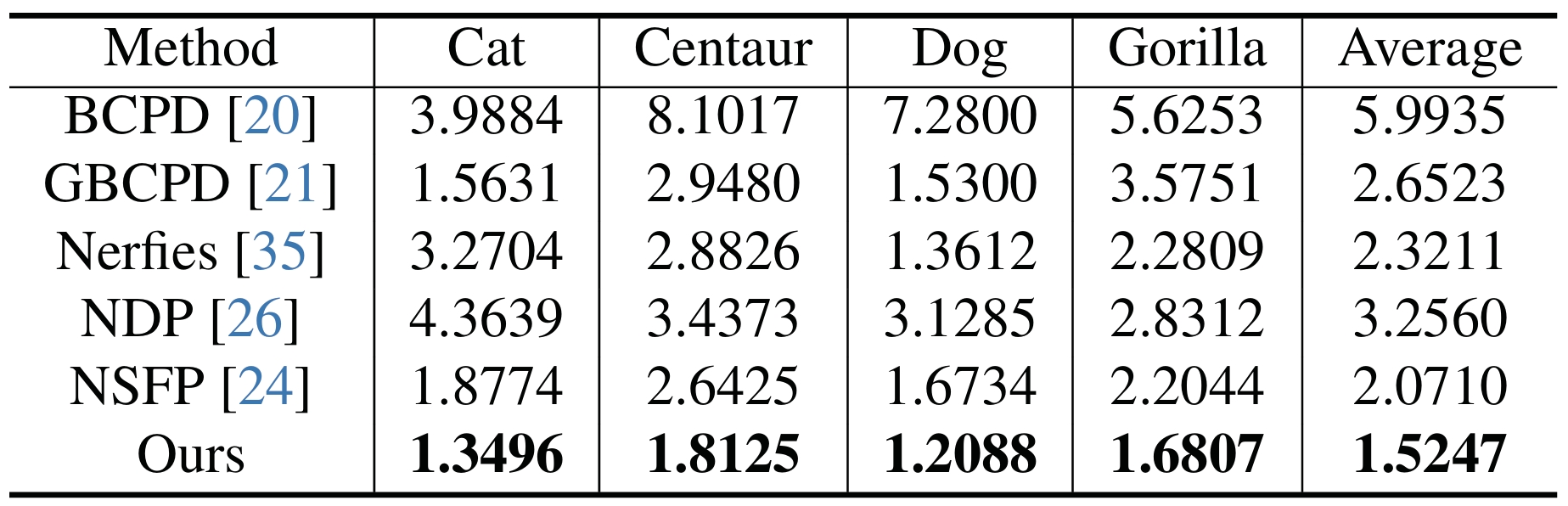
Quantitative comparisons on the TOSCA dataset.
Applications
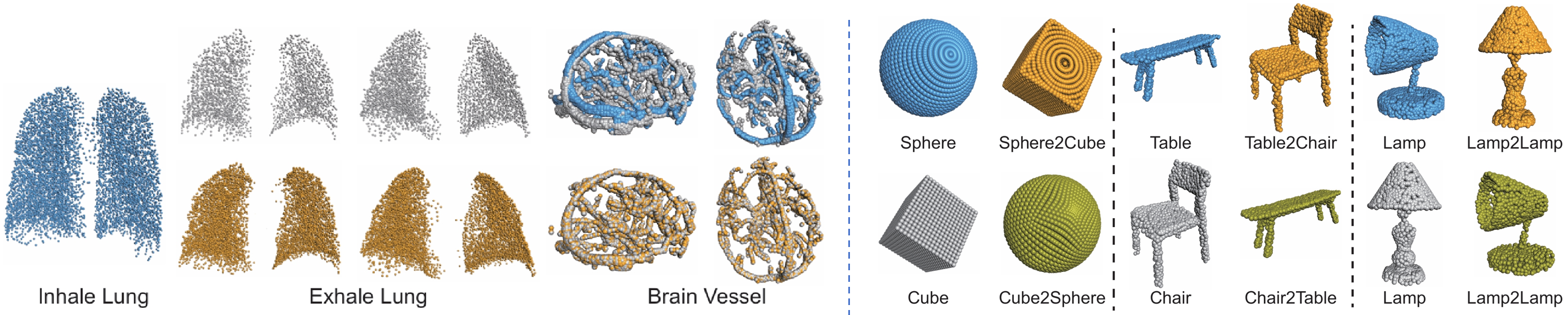
Left: Application of our method to medical data registration. Right: Application of the proposed method to shape transfer.
Citation
@inproceedings{zhao2024clustereg,
title={Correspondence-Free Nonrigid Point Set Registration Using Unsupervised Clustering Analysis},
author={Mingyang Zhao, Jingen Jiang, Lei Ma, Shiqing Xin, Gaofeng Meng, Dong-Ming Yan},
booktitle={Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition},
year={2024}
}






